Getting started with the Search API
In this tutorial you perform your first query with the Collibra REST Search API. You use wildcard characters to expand your search and filters to refine it.
curl -X POST 'https://<your_collibra_url>/rest/2.0/search' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"keywords": "issue"
}'All of the examples in this tutorial work with the out-of-the-box resources created during the installation of the Collibra platform.
Prerequisites
- Access to Collibra.
- Postman or an alternative HTTP API client.
Some references might be specific to the Postman application.
For more information on how to install Postman and establish an authentication session, see the Collibra REST API authentication tutorial.
About the Collibra REST Search API
The Search API allows you to take advantage of the same engine that powers the Collibra user interface search. It uses the same wildcard characters as the UI search and the search results are influenced by the same Search index configuration settings in Console.
The UI search appends wildcard * setting only applies to the UI search without any impact on the API search. If set (default), it can lead to the same search having different results in Collibra and the Search API.
The search request
The search request is a JSON object. The simplest request contains the only mandatory field that represents the search term:
{
"keywords": "search term"
}Wildcards
To expand your search, you can use the same wildcard characters available in the user interface search.
|
Wildcard character |
Usage |
Search example |
Result example |
|---|---|---|---|
?
|
Replaces exactly one character. | iss?e
|
issue |
*
|
Replaces none or more characters. | compl*
|
completeness, compliance |
&&
|
Act as an AND operator. Returns results that contain all the search terms.
|
new && data
|
New Reference Data and New Data Assets |
" "
|
Performs an exact search.
|
\"policy issue\"
|
Data Policy Issue but not Policy non Compliance Issue or Policy |
curl -X POST 'https://<your_collibra_url>/rest/2.0/search' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"keywords": "\"policy issue\""
}Filters
You can narrow down you search results by indicating what kind of resource to return or where to look for the search term in a resource.
|
Filter |
Field name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Search filter | filters
|
A filter to refine the search results based on specific types, statuses, dates and tags of the returned resources. |
| Search in fields | searchInFields
|
A filter to refine the search results based on the occurrence of the search term in specific fields of resource types. |
You can use both types of filters at the same time.
Search filter
The search filter is an array of objects made up of field and values pairs:
curl -X POST 'https://<your_collibra_url>/rest/2.0/search' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"keywords": "data",
"filters": [
{
"field": "assetType",
"values": ["00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031112"]
}
]
}'You can combine each field value with certain values values:
|
|
|
Result |
|---|---|---|
| community | One or more community UUIDs | Only resources that belong to the selected communities, excluding communities. |
| domain | One or more domain UUIDs | Only resources that belong to the selected domains, excluding domains and communities. |
| domainType | One or more domain type UUIDs | Only domains that are of the selected domain type. |
| assetType | One or more asset type UUIDs | Only assets that are of the selected asset types. |
| status | One or more status UUIDs | Only assets that have the selected statuses. |
| createdBy | One or more user UUIDs | Only resources created by the selected users. |
| lastModifiedOn | Exactly one of the following values: LAST_24H, LAST_7D, LAST_30D, LAST_365D, OLDER_THAN_365D |
Only resources that were last modified in the selected time period. |
| createdOn | Only resources that were created in the selected time period. | |
| tags | One or more tags | Only assets with the selected tags. |
| certified | true or false |
Only assets with the certified flag. |
| rating | Exactly one of the following values: unrated, one_or_more_stars, two_or_more_stars, three_or_more_stars, four_or_more_stars |
Only assets with the selected rating. |
The field / values pairs are joined using the logical AND operator, unless the same key is repeated and they are joined using the OR operator. The elements of the values arrays are joined using the logical OR operator.
Some combinations will not return results because the filters refer to different types of resources, for example a combination of domainType and tags returns 0 results because domains do not have tags.
Search in fields
The search in fields filter is an array of objects consisting of resourceType and fields pairs:
curl -X POST 'https://<your_collibra_url>/rest/2.0/search' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"keywords": "data",
"searchInFields": [
{
"resourceType": "domain",
"fields": ["name"]
}
]
}'You can combine each resourceType value with certain fields values:
|
|
|
Result |
|---|---|---|
| community | Possible values are name and comments |
Only communities that have the search term in their name or comments. |
| domain | Only domains that have the search term in their name or comments. | |
| asset | Possible values are name, displayName, comments, tags, dataClassification, attributes and attribute:<attribute_type_UUID> |
Only assets that have the search term in the selected fields. attributes refers to all the attribute types of an asset while the pair attribute:<attribute_type_UUID> only refers to one specific attribute type. |
| user | name
|
Only users that have the search term in their name. |
| userGroup | Only user groups that have the search term in their name. |
The resourceType / fields pairs are joined using the logical OR operator. For the request to be valid, if one of the fields values is available for the other pairs, it must be present in all the pairs.
The equivalent of name for asset is displayName.
|
Example |
Valid |
Reason |
|---|---|---|
|
Yes | The only common fields value for the pairs is name and both pairs contain it. |
|
No |
The equivalent of
The correct pair should be: |
The elements of the fields arrays are joined using the logical OR operator.
The Search API REST call
To perform a search, use the POST method and the /search endpoint of the Search resource.
There are no parameters but you must include the JSON body.
curl -X POST 'https://<your_collibra_url>/rest/2.0/search' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"keywords": "issue",
"searchInFields": [
{
"resourceType": "domain",
"fields": ["name"]
}
]
}'The response contains the total number of results and the details for each result.
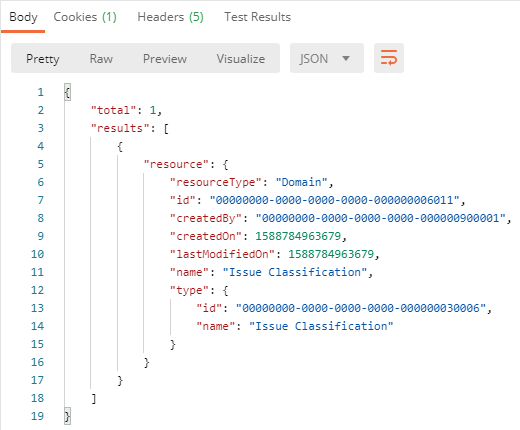
Summary
By following this tutorial:
- You have learned about the following components of the Collibra REST Search API:
- The JSON object.
- Wildcard characters.
- The search filter.
- The search in fields filter.
- The API call.
Additional resources
- Consult the Collibra REST Import API documentation provided with your version of Collibra Data Governance Center at https://<your_collibra_url>/api-docs/index.html?urls.primaryName=search-api.